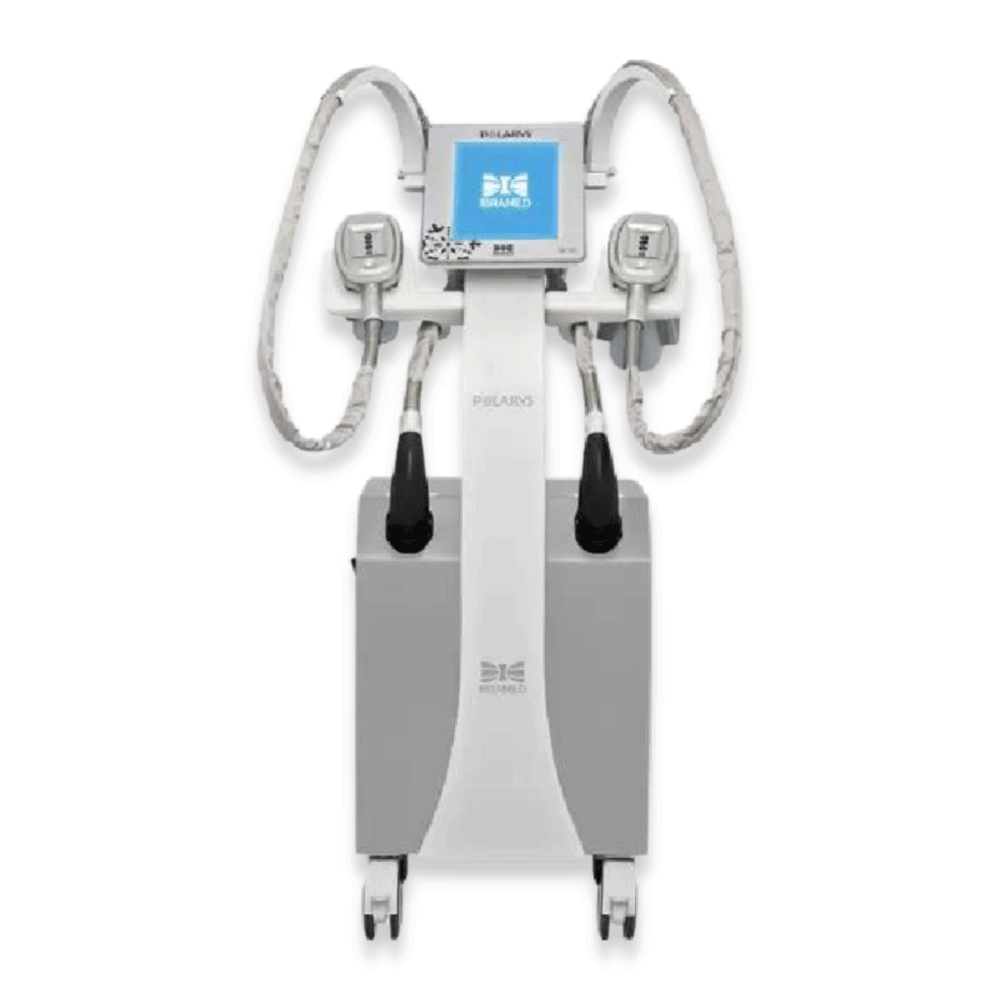
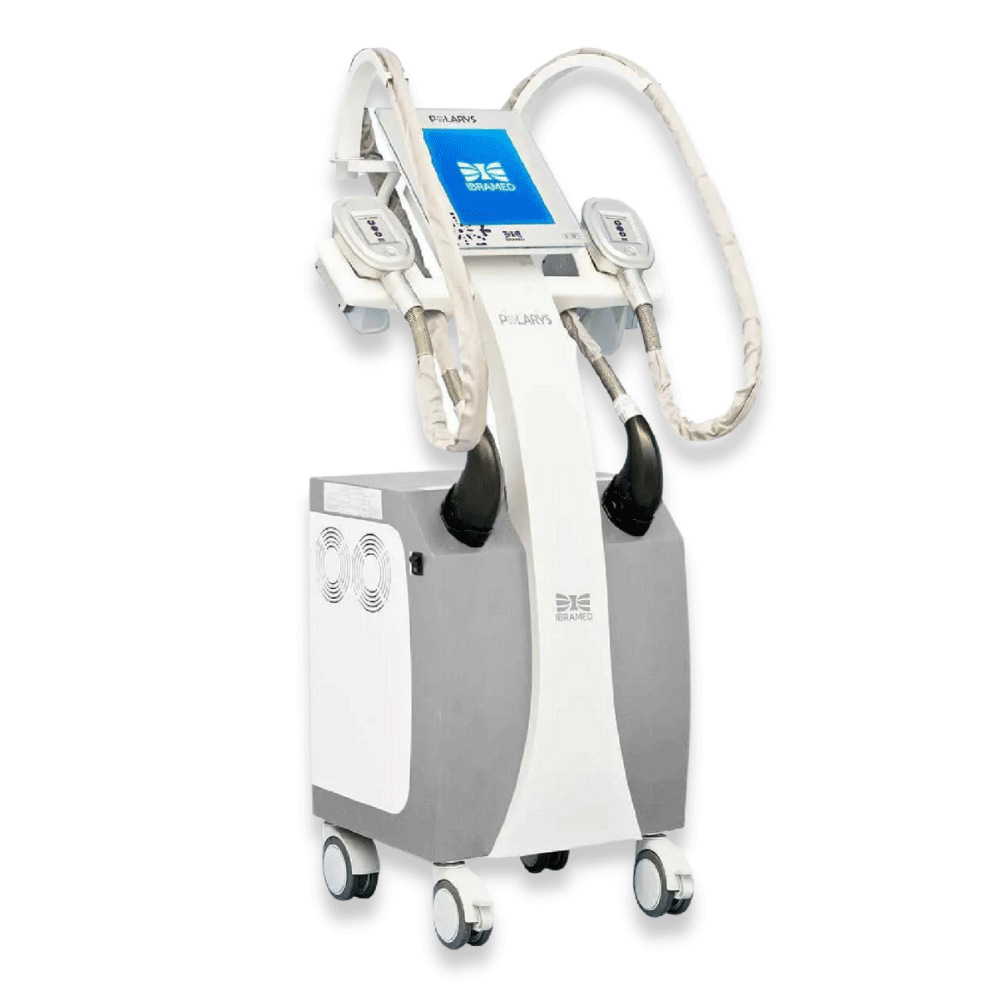
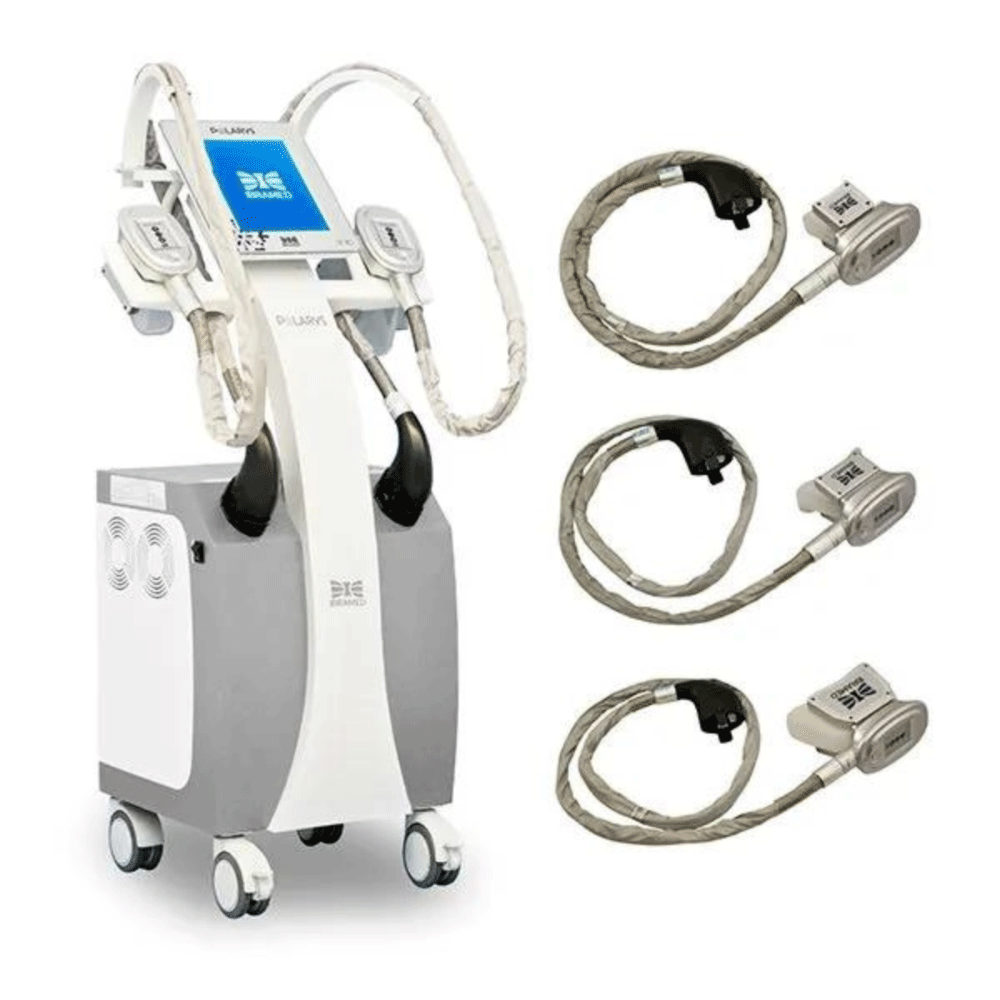
Polarys
Cryolipolysis
Product Code : 01061015
POLARYS is an advanced technology aimed at the treatment of localized fat and non-invasive body contouring through the innovative cryolipolysis system.
Request a Quote
The equipment has 4 treatment modalities:
- Conventional Cryolipolysis
- Contrast
- Reperfusion
- Preparation
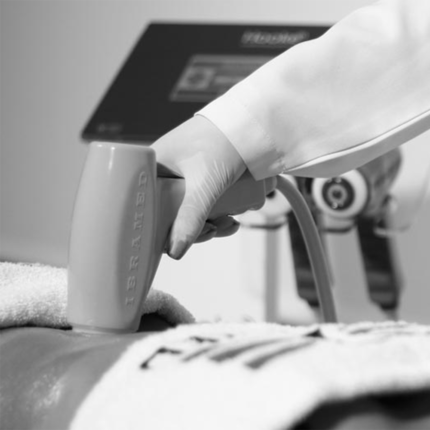
It is a safe treatment for presenting an effective cooling system that guarantees the stability of the selected temperature during the simultaneous use of both applicators throughout the treatment time.
Indications Treatment of localized fat
- Treatment of fat located in the submentum
- Treatment of localized fat in small areas, as well as: pubis, anterior and posterior axillary region, infrascapular, inner knee, infragluteal, lumbar region and arms.
- Contraindications for Pregnant women. Implanted electronic device (eg, pacemaker).
- Neoplastic areas or over areas where the tumor has been removed.
- Children, the elderly, or patients with high sensitivity to cold (cryoglobulinemia). Cryotherapy intolerance. Raynaud’s Syndrome.
For Ischemic areas (where the blood supply may be unable to meet the metabolic demand resulting in necrosis).
For open or infected wounds. Relative about abdominal hernia for patients treated in the abdomen. Diabetes Mellitus or other cases of scarring deficit. Individuals with metabolic and liver diseases that compromise fat metabolism.
For areas with altered sensitivity.
- On irritated skin or with the presence of dermatitis.
- Recent surgery at the treatment site. Regular use of anti-inflammatory medications.
- Keloids or keloid propensity in the region to be treated.
- Regions with marks of hypertrophic scars.
Infraumbilical abdomen (Properly protect the umbilicus region.)
- Flanking region
- Inner thigh region
- Glass region
- Infrascapular region
- Lumbar region
- Back arm region
- Infragluteal region
- Anterior axillary region
- Posterior axillary region
- Inner knee region
- Subment region.
- 1 PP female I.E.C cable of 3 x 0.75 x 1500mm (Code 03017007)
- 2 5A 20 AG fuses (Code 03019012)
- 1 Polarys Digital Operations Manual (Code 03004002)
- 1 ruler for marking applicator P (Code 03027467)
- 1 ruler for marking M applicator (Code 03027468)
- 1 ruler for marking G applicator (Code 03027469)
- 3 applicators (check the reseller at the time of purchase)
- 3 antifreeze membranes (03026127)
Physiology
1. Crystallization of lipids (caused by cold).
2. Inflammatory panniculitis (inflammation produced by cold).
3. Programmed Cell Death and Phagocytosis – Gradual removal of cellular waste by natural mechanisms (neurophils and macrophages).
4. Decreased number of adipocytes and body remodeling
5. Reperfusion injury (by reactive oxygen species).
Crystallization of lipids: A certain temperature extraction (approximately +8 °C) induces the crystallization of fat contained in adipocytes. This effect triggers cell death in adipocytes that are much more susceptible to cold than other cells in the skin and subcutaneous tissue. The effects induced by crystallization are irreversible.
Inflammatory panniculitis: the inflammatory process caused in adipocytes by crystallization and subsequent reperfusion is reflected by the flow of inflammatory cells that can be observed around the 3rd day after treatment and peaks on approximately the 14th day with the presence of infiltrate containing histiocytes, neutrophils, lymphocytes and other mononuclear cells.
Gradual removal of cellular debris by phagocytes: Between the 14th and 30th day post-treatment, macrophages and other phagocytes engulf and digest fat cells as part of a natural response to injury. Decreased number of adipocytes and body remodeling: 4 weeks after treatment, inflammation and adipocyte volume decrease. Between 2 to 3 months after treatment, the interlobular septa thicken and the inflammatory process disappears.
Reperfusion injury: Tissue damage caused when the blood supply returns to the tissue after a period of ischemia or lack of oxygen. The dynamics between vascular stasis and tissue reperfusion induces the production of ROS (reactive oxygen species). The absence of oxygen and nutrients from the blood during the cooling period creates a condition in which the restoration of circulation results in inflammation and oxidative damage through the induction of oxidative stress, rather than the restoration of normal function.